How AI Helped Create an Engaging, AI-Resistant Learning Experience
A step-by-step guide to using AI tools for innovative assignment redesign
As educators, we face a dual mandate: embracing AI's potential to enhance learning while adapting to the reality that this next technology will require changes to our course delivery and assessments. This blog explores how I used AI to redesign an assignment and integrate a new teaching approach, creating a richer student experience and an assignment more resistant to the misuse of AI tools. AI helped me transform a static project into an interactive, real-world simulation that fosters critical thinking and collaboration.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Original “Store Check” Assignment
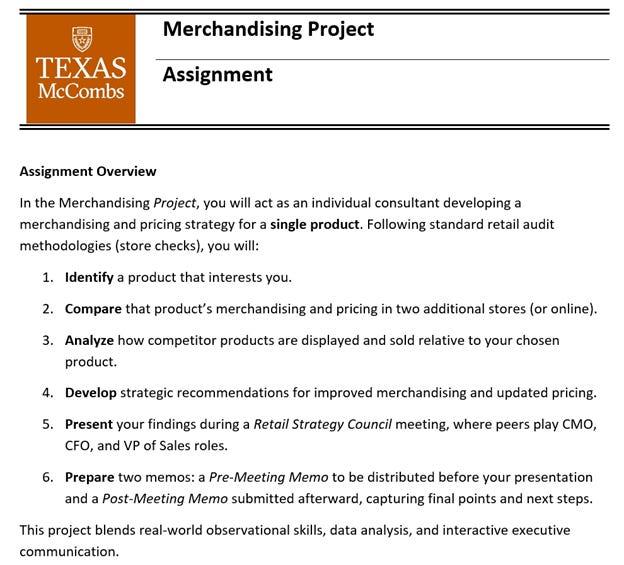
In an undergraduate marketing elective on channel strategy, I previously assigned a "store check" project where students visit retail stores, analyze the merchandising of a specific product, and submit a written report. While this project honed observational skills and introduced students to retail concepts such as shelf placement and pricing strategies, it had limitations:
Limited Interactivity: No opportunity for peer collaboration or real-time feedback.
AI Vulnerability: Written reports were susceptible to being generated by AI tools, undermining the learning process.
Missing Executive Skill Development: The original assignment structure did not require students to practice executive-level decision-making or persuasive communication, skills critical in business careers.
These shortcomings highlighted the need for a more dynamic and engaging approach that could address these gaps while leveraging AI responsibly.
Inspiration for Change
My inspiration for restructuring the project was an approach developed by my friend and colleague, McCombs Marketing professor Bill Peterson. This approach was recently published in a paper co-authored with Brandon Campitelli, Assistant Director of the McCombs Office of Instructional Innovation, “Scrap the Final Paper or Presentation—Lead a Simulated Meeting Instead.” Bill’s innovation involves creating a Simulated Leadership Meeting (SLM) structure that mimics real-world business meetings where stakeholders debate recommendations and forge consensus.
This SLM format inspired me to reimagine the store check assignment as a simulated leadership experience with these goals:
Foster collaboration and critical thinking.
Expose students to peer work through interactive discussions.
Enhance executive skills like persuasion and analysis in realistic settings.
Reduce reliance on rote AI use while encouraging productive applications of AI tools.
How AI Helped Redesign the Assignment
To bring this vision to life, I used AI as my design partner to integrate insights from Bill’s white paper on SLMs with best practices for conducting store checks in retail.
Step 1. Generating Initial Project Outline
I uploaded three documents into the AI tool Perplexity.ai running the O3-mini LLM model:
The instructions for my original store check assignment.
A best practices article on conducting store checks in retail that I planned to assign to students as a reading
A white paper Bill wrote on Simulated Leadership Meetings.
Using this input, I wrote a prompt using well-crafted prompts asking AI to propose an outline for a project that combined elements of both assignments into a phased project with clear steps: product selection, store visits, data analysis, presentation preparation, and an interactive meeting simulation. In this first prompt, I only asked for an outline for the project that I could review to ensure that the AI tool had all of the key elements. A shortened version of the prompt I used:
As an expert in marketing and course design, help me create an individual student project for my undergraduate marketing elective on channel strategy where students select one product at a store, conduct store checks at three stores, compare merchandising and pricing, and present recommendations in a simulated leadership meeting.
Use these documents:
Store Check Assignment.pdf – the previous version of this project, that was more general, not just focused on the UT Co-op
How to Conduct Store Checks in Retail.pdf – a reading I will assign to students with details on how to do a store check
Simulated Leadership Meeting White Paper - 2023-10-06.pdf – a note that outline the approach we will use for student deliverables on this project, the note anticipates a group project, but this will be an individual project, students will work to persuade an executive team of peer students randomly assigned to role of CMO, CFO, and VP of Sales
Start by preparing a detailed outline of the project structure, including key steps.
Propose five alternative titles for the project and five alternative names for the simulated leadership meeting format.The proposed outline was strong, and I selected “Retail Strategy Council” (RSC) from the project names proposed in the response.
Step 2. Crafting Detailed Instructions
Next, I asked the AI to draft instructions for the redesigned project.
Great so far. For this thread we will refer to the project as "Merchandising Project"
Each student will present to a Retail Strategy Council, an executive team of peer students randomly assigned to role of CMO, CFO, and VP of Sales
Now write detailed instructions for this assignment of about 1000 words that describe the project, the learning objectives, define key concepts, that students will complete a two-page memo using a template we will create in the prompt (the template should be patterned after the example in the Simulated Leadership Meeting White Paper, and that the project will be scored based on evaluations by the Retail Strategy Council and instructor scoring of both the post-memo.The AI tool responded with:
Learning objectives focused on retail merchandising fundamentals, pricing strategies, and executive communication skills.
Key deliverables include pre-meeting memos, live presentations, and post-meeting reflections modeled after SLM templates.
Scoring criteria for evaluating both individual performance and group engagement.
Step 3. Developing Templates
In the last prompt, I asked AI to generate templates for the pre-meeting memo students would submit as an assignment and share with their RSC executives, as well as a template for the post-meeting memo students would revise based on their discussion. I also asked AI to rewrite the assignment instructions from the previous step to reflect the titles and structure of the templates created in this step.
Using the structure in the Simulated Leadership Meeting White Paper create templates for both pre-meeting memo and the post-meeting memo. Then rewrite the instructions using all of the some information above, but adding the post-meeting memo the process and instructionsThese structured documents guided students in summarizing their findings while preparing them for interactive discussions with peers acting as executives
4. Human Oversight and Customization
While the AI provided an excellent starting point, its outputs required extensive editing to align with my course goals and pedagogical philosophy. For example:
refining the roles assigned to students during simulations (e.g., Channel Manager presenting to peers as CMO, CFO, and VP of sales)
expanding some instructions to have more detail
adjusting scoring rubrics to emphasize critical thinking and adaptability during live discussions
This iterative process ensured the final assignment was rigorous and tailored to my students’ needs.
The Transformed Assignment
The redesigned project—now called the Retail Strategy Council—now had four components:
Store Check Instructions: Best practices and a template for conducting store checks similar to the original project.
Pre-Meeting Memos: The assignment required students to use a template to prepare concise summaries of their findings and recommendations before their presentations.
Simulated Leadership Meetings: In small groups, students presented their analyses to peers role-playing as executives who challenged their ideas with questions or alternative perspectives.
Post-Meeting Memos: After their meeting, students submitted a reflection on the feedback received during discussions and refined their recommendations accordingly.
This format mirrored real-world business scenarios and encouraged deeper engagement with course material.
Implementation and Outcomes
Students enthusiastically embraced their roles during simulations. They presented findings on merchandising gaps or pricing strategies and defended their recommendations against peer critiques.
After students had submitted their post-meeting memos, I had them complete a feedback survey. The response was overwhelmingly positive:
Students appreciated the interactive format that mimicked real-world business meetings.
They found value in applying theoretical concepts practically while honing soft skills like persuasion and adaptability.
“A valuable experience that prepares us for our future roles and helps us understand that making decisions requires feedback and recommendations.” — Student survey response
Encouraged by the success of SLM for this project, I plan to use this same approach to adapt a pricing project to SLM format later in the semester.
Using AI to redesign this project
Benefits
Efficiency: AI accelerated assignment design by synthesizing diverse inputs into a coherent first draft for editing.
Innovation: The alternatives generated by AI encouraged me to rethink my project structure and learning objectives creatively.
Broader Implications for Educators
How can we embrace AI as a tool for innovation rather than viewing it solely as a threat? By designing assignments that promote active learning and critical thinking, we can harness its potential while thoughtfully addressing its limitations.
Redesigning assignments with AI allows educators to enhance learning outcomes while addressing challenges posed by generative tools like ChatGPT. In my case, integrating Biill Peterson’s SLM framework with insights from retail best practices transformed a static project into an engaging simulation that mirrors real-world dynamics.
As educators in an era of rapid technological change, AI tools can help us innovate efficiently and effectively. Not just reacting to these new technologies but improving learning. We can prepare our students for success by embracing this challenge creatively and collaborating with our colleagues and AI tools.